
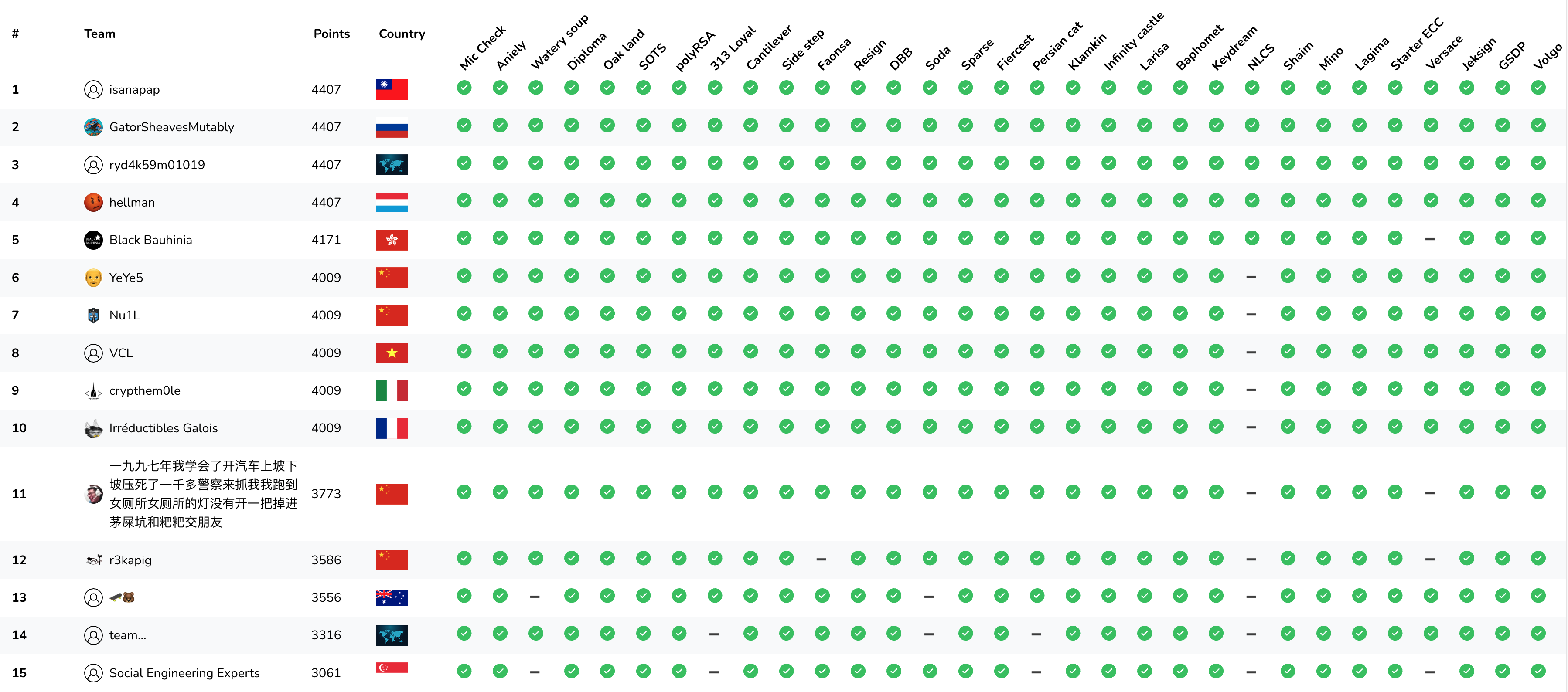
I participated in the Crypto CTF 2022 event (a CTF which contains only cryptography related challenges), playing as part of Social Engineering Experts. It occurred over the course of 1 day (Fri, 15 July 2022, 22:00 SGT — Sat, 16 July 2022, 22:00 SGT). In the end, we ranked 15th out of 421 scoring teams :
Neobeo and Julia Poo solved most of the difficult challenges and I definitely learnt a lot from them, especially from Neobeo’s solution to Soda which involved Egyptian fractions :
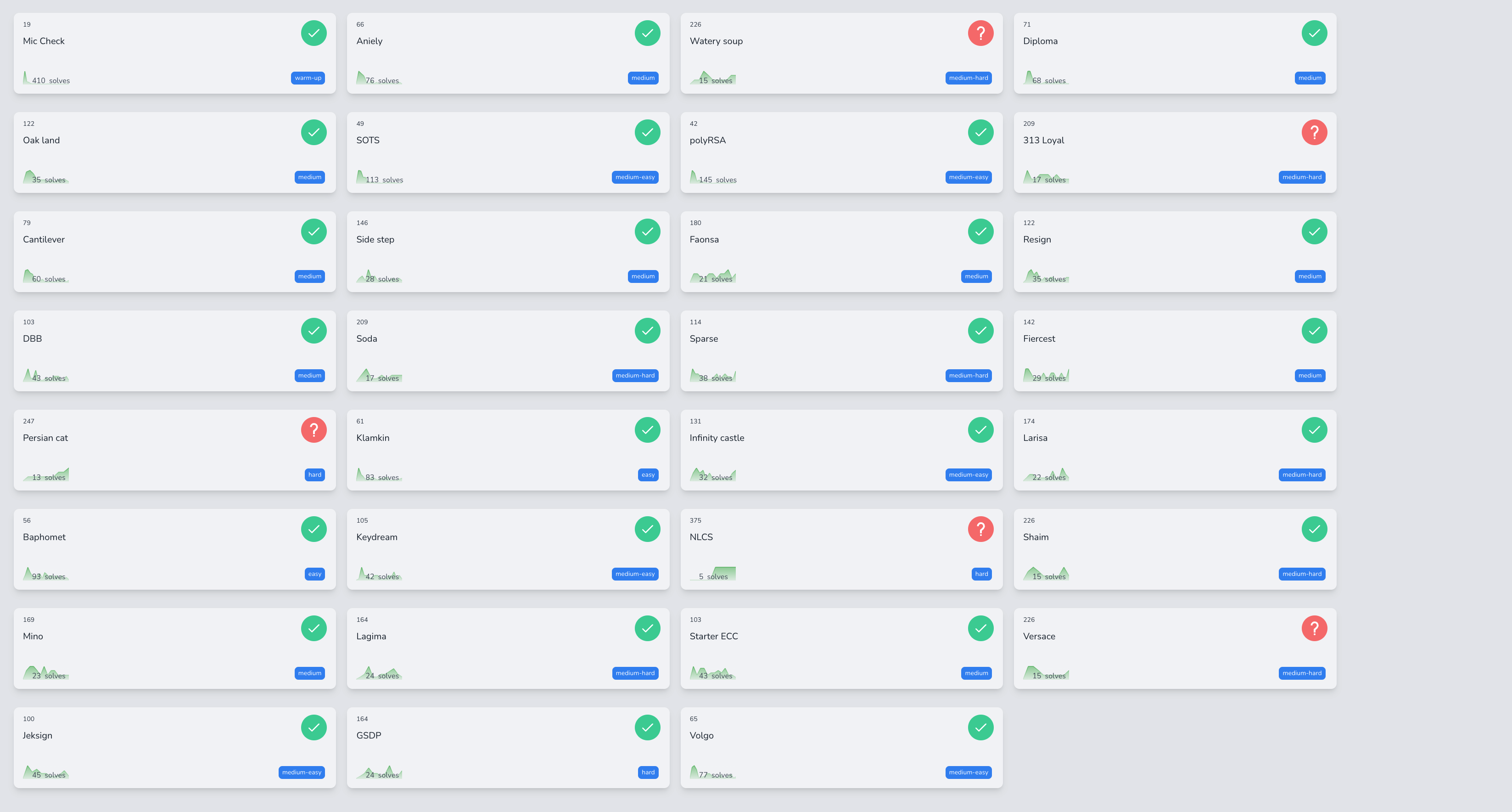
All attached challenge files can be found here.Below are the writeups :
| Challenge | Category | Points | Solves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mino | Crypto | 169 | 23 |
| Sparse | Crypto | 114 | 38 |
| Keydream | Crypto | 105 | 42 |
| Jeksign | Crypto | 100 | 45 |
| Diploma | Crypto | 71 | 68 |
| Baphomet | Crypto | 56 | 93 |
| SOTS | Crypto | 49 | 113 |
| polyRSA | Crypto | 42 | 145 |
| Mic Check | Misc | 19 | 410 |
Mino

The source code :
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import sys
from flag import flag
def die(*args):
pr(*args)
quit()
def pr(*args):
s = " ".join(map(str, args))
sys.stdout.write(s + "\n")
sys.stdout.flush()
def sc():
return sys.stdin.readline().strip()
def main():
border = "|"
pr(border*72)
pr(border, "Hi crypto programmers! I'm looking for some very special permutation", border)
pr(border, "p name MINO such that sum(p(i) * (-2)^i) = 0 from 0 to n - 1, for ", border)
pr(border, "example for n = 6, the permutation p = (4, 2, 6, 5, 3, 1) is MINO: ", border)
pr(border, "4*(-2)^0 + 2*(-2)^1 + 6*(-2)^2 + 5*(-2)^3 + 3*(-2)^4 + 1*(-2)^5 = 0 ", border)
pr(border, "In each step find such permutation and send to server, if there is ", border)
pr(border, "NOT such permutation for given n, just send `TINP', good luck :) ", border)
pr(border*72)
step, final = 3, 40
while True:
pr(border, f"Send a MINO permutation of length = {step} separated by comma: ")
p = sc().split(',')
if step % 3 == 1:
if p == ['TINP']:
if step == final: die(border, f"Congrats, you got the flag: {flag}")
else:
pr(border, "Great, try the next level :)")
step += 1
else:
die(border, "the answer is not correct, bye!!!")
elif len(p) == step:
try:
p = [int(_) for _ in p]
except:
pr(border, "the permutation is not valid")
if set(p) == set([_ for _ in range(1, step + 1)]):
S = 0
for _ in range(step):
S += p[_] * (-2) ** _
if S == 0:
if step == final:
die(border, f"Congrats, you got the flag: {flag}")
else:
pr(border, "Great, try the next level :)")
step += 1
else:
die(border, "the answer is not correct, bye!!!")
else:
pr(border, "the permutation is not valid!!!")
else:
die(border, f"the length of permutation is not equal to {step}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Solve script :
#Through Bruteforce
n3 = (2, 3, 1)
n4 = 'TINP'
n5 = (2, 3, 5, 4, 1)
n6 = (2, 3, 5, 6, 4, 1)
n7 = 'TINP'
n8 = (2, 1, 4, 6, 8, 5, 7, 3)
n9 = (2, 1, 4, 6, 8, 5, 7, 9, 3)
#Construct Pattern
sl = [n3, n4, n5, n6, n7, n8, n9]
def checkPerm(perm, n):
S = 0
for _ in range(n):
S += perm[_] * (-2) ** _
if S == 0:
#print(f"Passed check, {perm=}")
return True
return False
width = 0
for n in range(10,41,3):
if (n % 3 == 1):
sl.append('TINP')
width += 1
np1 = list(sl[-2])[:-width] + [n+1, n] + list(sl[-2])[-width:]
#print(f"{np1=}")
np2 = list(sl[-2])[:-width] + [n+1, n+2, n] + list(sl[-2])[-width:]
sl.append(np1)
sl.append(np2)
assert checkPerm(tuple(np1), len(np1)) == True and checkPerm(tuple(np2), len(np2))
print(f"{sl=}")
from pwn import *
debug = True
r = remote("02.cr.yp.toc.tf", 13771, level = 'debug' if debug else None)
for sol in sl:
if sol == 'TINP':
r.sendlineafter(b'separated by comma: \n', sol)
else:
r.sendlineafter(b'separated by comma: \n', str(sol)[1:-1])
print(r.recvall())
#b'| Congrats, you got the flag: CCTF{MINO_iZ_4N_3a5Y_Crypto_C0d!n9_T4sK!}\n'
Flag : CCTF{MINO_iZ_4N_3a5Y_Crypto_C0d!n9_T4sK!}
Sparse

The source code :
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from flag import flag
def sparse(p, k):
nbit = p.bit_length()
while True:
CF = [getRandomRange(-1, 1) for _ in '_' * k]
XP = [getRandomRange(3, nbit - 3) for _ in '_' * k]
A = sum([CF[_] * 2 ** XP[_] for _ in range(0, k)])
q = p + A
if isPrime(q) * A != 0:
return q
p = getPrime(417)
q = sparse(p, 5)
e, n = 65537, p * q
print(f'n = {n}')
m = bytes_to_long(flag.encode('utf-8'))
assert m < n
c = pow(m, e, n)
print(f'c = {c}')
The solve script (got third blood) :
from tqdm import tqdm
from Crypto.Util.number import *
n = 94144887513744538681657844856583985690903055376400570170371837200724227314957348031684706936655253125445176582486308241015430205703156336248578475428712275706238423997982248462635972817633320331030484841129628650918661036694615254018290264619628335177
ct = 80250313885079761377138486357617323555591919111371649902793873860183455237161293320577683249054725852540874552433031133240624696119120378419135912301004715004977978507247634217071922495893934816945961054193052791946557226599493364850793396744903765857
for i in tqdm(range(1000)):
for j in (range(1000)):
A = -1*(2^i)*(1+2^j)
R.<p> = PolynomialRing(QQ)
poly = p^2 + A*p - n
try:
p = poly.roots()[0][0]
except IndexError:
continue
if n % p == 0:
q = p + A
φ = (p-1) * (q-1)
e = 65537
d = pow(e, -1, φ)
print(long_to_bytes(pow(ct, d, n)))
exit()
#b'CCTF{5pArs3_dIfFeRenc3_f4ct0r1za7iOn_m3th0d!}'
Flag : CCTF{5pArs3_dIfFeRenc3_f4ct0r1za7iOn_m3th0d!}
Keydream

The source code :
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import string
from flag import flag
def randstr(l):
rstr = [(string.printable[:62] + '_')[getRandomRange(0, 62)] for _ in range(l)]
return ''.join(rstr)
def encrypt(msg, l):
while True:
rstr = 'CCTF{it_is_fake_flag_' + randstr(l) + '_90OD_luCk___!!}'
p = bytes_to_long(rstr.encode('utf-8'))
q = bytes_to_long(rstr[::-1].encode('utf-8'))
if isPrime(p) and isPrime(q):
n = p * q
e, m = 65537, bytes_to_long(msg.encode('utf-8'))
c = pow(m, e, n)
return n, c
n, c = encrypt(flag, 27)
print(f'n = {n}')
print(f'c = {c}')
Solve script :
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import logging
from math import gcd
from sage.all import ZZ
from sage.all import QQ
from sage.all import Sequence
from sage.all import gcd
from sage.all import matrix
from sage.all import solve
from sage.all import var
from sage.all import Zmod
from math import ceil
from math import log
from math import pi
from math import sqrt
from PartialInteger import PartialInteger
#https://github.com/jvdsn/crypto-attacks
DEBUG_ROOTS = None
def fill_lattice(shifts, monomials, bounds):
"""
Creates a lattice basis containing the coefficients of the shifts in the monomials.
:param shifts: the shifts
:param monomials: the monomials
:param bounds: the bounds
:return: the lattice basis
"""
logging.debug(f"Filling the lattice ({len(shifts)} x {len(monomials)})...")
B = matrix(ZZ, len(shifts), len(monomials))
for row, shift in enumerate(shifts):
for col, monomial in enumerate(monomials):
B[row, col] = shift.monomial_coefficient(monomial) * monomial(*bounds)
return B
def reduce(B):
"""
Reduces a lattice basis using a lattice reduction algorithm (currently LLL).
:param B: the lattice basis
:return: the reduced basis
"""
logging.debug("Executing the LLL algorithm...")
return B.LLL()
def reconstruct_polynomials(B, f, monomials, bounds, preprocess_polynomial=lambda x: x, divide_original=True):
"""
Reconstructs polynomials from the lattice basis in the monomials.
:param B: the lattice basis
:param f: the original polynomial
:param monomials: the monomials
:param bounds: the bounds
:param preprocess_polynomial: a function which preprocesses a polynomial before it is added to the list (default: identity function)
:param divide_original: if set to True, polynomials will be divided by f if possible (default: True)
:return: a list of polynomials
"""
logging.debug("Reconstructing polynomials...")
polynomials = []
for row in range(B.nrows()):
polynomial = 0
for col, monomial in enumerate(monomials):
assert B[row, col] % monomial(*bounds) == 0
polynomial += B[row, col] * monomial // monomial(*bounds)
polynomial = preprocess_polynomial(polynomial)
if divide_original and polynomial % f == 0:
logging.debug(f"Original polynomial divides reconstructed polynomial at row {row}, dividing...")
polynomial //= f
# TODO: how to check if the polynomials are pairwise algebraically independent? Divide out GCDs?
if polynomial.is_constant():
logging.debug(f"Polynomial at row {row} is constant, ignoring...")
continue
if DEBUG_ROOTS is not None:
logging.debug(f"Polynomial at row {row} roots check: {polynomial(*DEBUG_ROOTS)}")
polynomials.append(polynomial)
logging.debug(f"Reconstructed {len(polynomials)} polynomials")
return polynomials
def find_roots_univariate(polynomial, x):
"""
Returns a generator generating all roots of a univariate polynomial in an unknown.
:param polynomial: the polynomial
:param x: the unknown
:return: a generator generating dicts of (x: root) entries
"""
if polynomial.is_constant():
return
for root in polynomial.roots(multiplicities=False):
if root != 0:
yield {x: int(root)}
def find_roots_gcd(polynomials, pr):
"""
Returns a generator generating all roots of a polynomial in some unknowns.
Uses pairwise gcds to find trivial roots.
:param polynomials: the reconstructed polynomials
:param pr: the polynomial ring
:return: a generator generating dicts of (x0: x0root, x1: x1root, ...) entries
"""
if pr.ngens() != 2:
return
logging.debug("Computing pairwise gcds to find trivial roots...")
x, y = pr.gens()
for i in range(len(polynomials)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(polynomials)):
g = gcd(polynomials[i], polynomials[j])
if g.degree() == 1 and g.nvariables() == 2 and g.constant_coefficient() == 0:
# g = ax + by
a = int(g.monomial_coefficient(x))
b = int(g.monomial_coefficient(y))
yield {x: b, y: a}
yield {x: -b, y: a}
def find_roots_groebner(polynomials, pr):
"""
Returns a generator generating all roots of a polynomial in some unknowns.
Uses Groebner bases to find the roots.
:param polynomials: the reconstructed polynomials
:param pr: the polynomial ring
:return: a generator generating dicts of (x0: x0root, x1: x1root, ...) entries
"""
# We need to change the ring to QQ because groebner_basis is much faster over a field.
# We also need to change the term order to lexicographic to allow for elimination.
gens = pr.gens()
s = Sequence(polynomials, pr.change_ring(QQ, order="lex"))
while len(s) > 0:
G = s.groebner_basis()
logging.debug(f"Sequence length: {len(s)}, Groebner basis length: {len(G)}")
if len(G) == len(gens):
logging.debug(f"Found Groebner basis with length {len(gens)}, trying to find roots...")
roots = {}
for polynomial in G:
vars = polynomial.variables()
if len(vars) == 1:
for root in find_roots_univariate(polynomial.univariate_polynomial(), vars[0]):
roots |= root
if len(roots) == pr.ngens():
yield roots
return
logging.debug(f"System is underdetermined, trying to find constant root...")
G = Sequence(s, pr.change_ring(ZZ, order="lex")).groebner_basis()
vars = tuple(map(lambda x: var(x), gens))
for solution_dict in solve([polynomial(*vars) for polynomial in G], vars, solution_dict=True):
logging.debug(solution_dict)
found = False
roots = {}
for i, v in enumerate(vars):
s = solution_dict[v]
if s.is_constant():
if not s.is_zero():
found = True
roots[gens[i]] = int(s) if s.is_integer() else int(s) + 1
else:
roots[gens[i]] = 0
if found:
yield roots
return
return
else:
# Remove last element (the biggest vector) and try again.
s.pop()
def find_roots_resultants(polynomials, gens):
"""
Returns a generator generating all roots of a polynomial in some unknowns.
Recursively computes resultants to find the roots.
:param polynomials: the reconstructed polynomials
:param gens: the unknowns
:return: a generator generating dicts of (x0: x0root, x1: x1root, ...) entries
"""
if len(gens) == 1:
if polynomials[0].is_univariate():
yield from find_roots_univariate(polynomials[0].univariate_polynomial(), gens[0])
else:
resultants = [polynomials[0].resultant(polynomials[i], gens[0]) for i in range(1, len(gens))]
for roots in find_roots_resultants(resultants, gens[1:]):
for polynomial in polynomials:
polynomial = polynomial.subs(roots)
if polynomial.is_univariate():
for root in find_roots_univariate(polynomial.univariate_polynomial(), gens[0]):
yield roots | root
def find_roots_variety(polynomials, pr):
"""
Returns a generator generating all roots of a polynomial in some unknowns.
Uses the Sage variety (triangular decomposition) method to find the roots.
:param polynomials: the reconstructed polynomials
:param pr: the polynomial ring
:return: a generator generating dicts of (x0: x0root, x1: x1root, ...) entries
"""
# We need to change the ring to QQ because variety requires a field.
s = Sequence([], pr.change_ring(QQ))
for polynomial in polynomials:
s.append(polynomial)
I = s.ideal()
dim = I.dimension()
logging.debug(f"Sequence length: {len(s)}, Ideal dimension : {dim}")
if dim == -1:
s.pop()
elif dim == 0:
logging.debug("Found ideal with dimension 0, computing variety...")
for roots in I.variety(ring=ZZ):
yield {k: int(v) for k, v in roots.items()}
return
def find_roots(polynomials, pr, method="groebner"):
"""
Returns a generator generating all roots of a polynomial in some unknowns.
The method used depends on the method parameter.
:param polynomials: the reconstructed polynomials
:param pr: the polynomial ring
:param method: the method to use, can be "groebner", "resultants", or "variety" (default: "groebner")
:return: a generator generating dicts of (x0: x0root, x1: x1root, ...) entries
"""
if pr.ngens() == 1:
logging.debug("Using univariate polynomial to find roots...")
for polynomial in polynomials:
yield from find_roots_univariate(polynomial, pr.gen())
else:
# Always try this method because it can find roots the others can't.
yield from find_roots_gcd(polynomials, pr)
if method == "groebner":
logging.debug("Using Groebner basis method to find roots...")
yield from find_roots_groebner(polynomials, pr)
elif method == "resultants":
logging.debug("Using resultants method to find roots...")
yield from find_roots_resultants(polynomials, pr.gens())
elif method == "variety":
logging.debug("Using variety method to find roots...")
yield from find_roots_variety(polynomials, pr)
def modular_univariate(f, N, m, t, X):
"""
Computes small modular roots of a univariate polynomial.
More information: May A., "New RSA Vulnerabilities Using Lattice Reduction Methods" (Section 3.2)
:param f: the polynomial
:param N: the modulus
:param m: the amount of normal shifts to use
:param t: the amount of additional shifts to use
:param X: an approximate bound on the roots
:return: a generator generating small roots of the polynomial
"""
f = f.monic().change_ring(ZZ)
pr = f.parent()
x = pr.gen()
delta = f.degree()
logging.debug("Generating shifts...")
shifts = set()
monomials = set()
for i in range(m):
for j in range(delta):
g = x ** j * N ** (m - i) * f ** i
shifts.add(g)
monomials.update(g.monomials())
for i in range(t):
h = x ** i * f ** m
shifts.add(h)
monomials.update(h.monomials())
L = fill_lattice(shifts, monomials, [X])
L = reduce(L)
polynomials = reconstruct_polynomials(L, f, monomials, [X])
for roots in find_roots(polynomials, pr):
yield roots[x],
def _get_shifts(m, x, k, shift, j, sum):
if j == len(x):
yield shift
else:
for ij in range(m + 1 - k - sum):
yield from _get_shifts(m, x, k, shift * x[j] ** ij, j + 1, sum + ij)
def sub(unknowns):
"""
Substitutes some values for the unknown components in this PartialInteger.
These values can be symbolic (e.g. Sage variables)
:param unknowns: the unknowns
:return: an integer or expression with the unknowns substituted
"""
i = 0
j = 0
shift = 0
#Hardcoded
#b'CCTF{it_is_fake_flag_' 168 bits MSB known
#b'_90OD_luCk___!!}' 128 bits LSB known
for value, bit_length in [(126573600356349647807173070852286652797, 128), (None, 216), (98304991485267288875783671426933398565429811701599, 168)]:
if value is None:
# We don't shift here because the unknown could be a symbolic variable
i += 2 ** shift * unknowns[j]
j += 1
else:
i += value << shift
shift += bit_length
return i
def factorize_p(N, beta=0.5, epsilon=0.125, m=None, t=None):
"""
Recover the prime factors from a modulus using Coppersmith's method and bits of one prime factor p are known.
More information: May A., "New RSA Vulnerabilities Using Lattice Reduction Methods" (Section 3.2)
More information: Herrmann M., May A., "Solving Linear Equations Modulo Divisors: On Factoring Given Any Bits" (Section 3 and 4)
:param N: the modulus
:param partial_p: the partial prime factor p (PartialInteger)
:param beta: the parameter beta (default: 0.5)
:param epsilon: the parameter epsilon (default: 0.125)
:param m: the number of normal shifts to use (default: automatically computed using beta and epsilon)
:param t: the number of additional shifts to use (default: automatically computed using beta and epsilon)
:return: a tuple containing the prime factors, or None if the factors could not be found
"""
n = 1 #Hardcoded
m = ceil(max(beta ** 2 / epsilon, 7 * beta)) if m is None else m
t = int(m * (1 / beta - 1)) if t is None else t
small_roots = modular_univariate
x = Zmod(N)[tuple(f"x{i}" for i in range(n))].gens()
f = sub(x)
X = 1 << 218 #Hardcoded
logging.info(f"Trying m = {m}, t = {t}...")
for roots in small_roots(f, N, m, t, X):
p = sub(roots)
if p != 0 and N % p == 0:
return p, N // p
return None
n = 23087202318856030774680571525957068827041569782431397956837104908189620961469336659300387982516148407611623358654041246574100274275974799587138270853364165853708786079644741407579091918180874935364024818882648063256767259283714592098555858095373381673229188828791636142379379969143042636324982275996627729079
ct = 3621516728616736303019716820373078604485184090642291670706733720518953475684497936351864366709813094154736213978864841551795776449242009307288704109630747654430068522939150168228783644831299534766861590666590062361030323441362406214182358585821009335369275098938212859113101297279381840308568293108965668609
p, q = factorize_p(n, m=6, t=6)
assert n == p*q
φ = (p-1) * (q-1)
e = 65537
d = pow(e, -1, φ)
print(long_to_bytes(pow(ct, d, n)))
#b'Congratz, the flag is: CCTF{h0M3_m4dE_k3Y_Dr1vEn_CrYp7O_5ySTeM!}'
Flag : CCTF{h0M3_m4dE_k3Y_Dr1vEn_CrYp7O_5ySTeM!}
Jeksign

The source code :
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from secret import gensol, nbit_gensol
from flag import flag
m = bytes_to_long(flag.encode('utf-8'))
print(m)
a = 1337
b = 31337
def die(*args):
pr(*args)
quit()
def pr(*args):
s = " ".join(map(str, args))
sys.stdout.write(s + "\n")
sys.stdout.flush()
def sc():
return sys.stdin.readline().strip()
def main():
border = "|"
pr(border*72)
pr(border, "Welcome crypto guys! Here we are looking for the solution of special", border)
pr(border, "Diophantine equation: 1337(z^4 - x^2) = 31337(y^2 - z^4) in natural ", border)
pr(border, "numbers, in each stage solve the equation in mentioned interval :) ", border)
pr(border*72)
STEP, level = 0, 19
while True:
p, q = nbit_gensol(1337, 31337, STEP + 30)
x, y, z = gensol(a, b, p, q)
pr(border, f"Send a solution like `x, y, z' such that the `z' is {STEP + 30}-bit: ")
ans = sc()
try:
X, Y, Z = [int(_) for _ in ans.split(',')]
NBIT = Z.bit_length()
except:
die(border, 'Your input is not valid, Bye!')
if 1337*(Z**4 - X**2) == 31337*(Y**2 - Z**4) and NBIT == STEP + 30:
if STEP == level - 1:
die(border, f'Congrats, you got the flag: {flag}')
else:
pr('| good job, try to solve the next challenge :P')
STEP += 1
else:
die(border, 'your answer is not correct, Bye!!')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Flag is printed at the start….. (got second blood)
Flag : CCTF{4_diOpH4nT1nE_3Qua7i0n_8Y_Jekuthiel_Ginsbur!}
Diploma

Chall description :
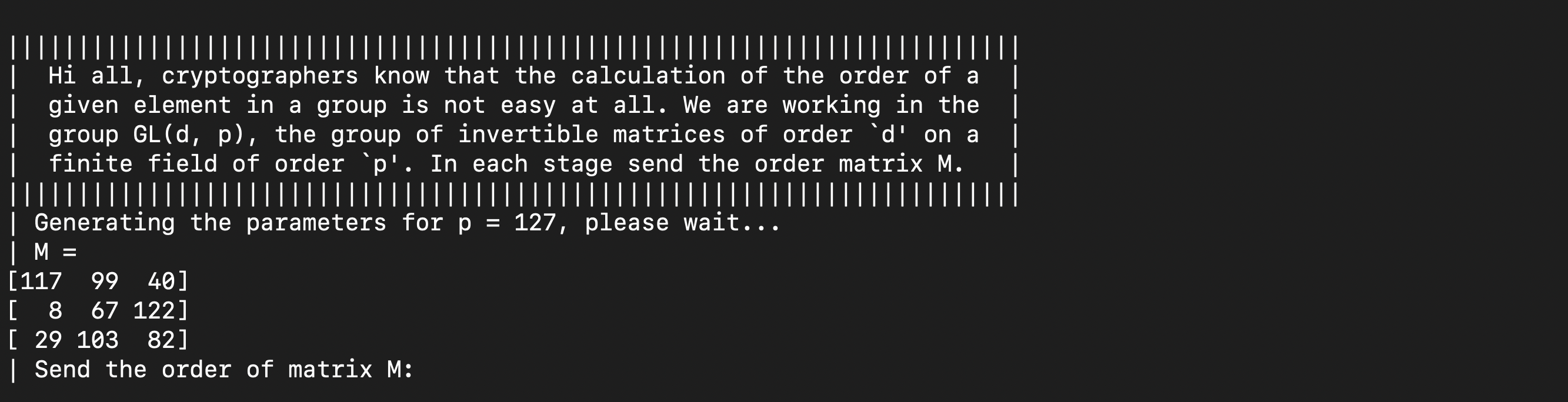
Solve script :
from pwn import *
import re
debug = True
r = remote("08.cr.yp.toc.tf", 37313, level = 'debug' if debug else None)
def parseMatrix(r, m):
r = re.sub(r"\s+", ",", re.sub(r"^\s+", "", r[1:-1], flags=re.UNICODE), flags=re.UNICODE)
m.append(eval("[" + r + "]"))
return m
for i in range(15):
r.recvuntil("please wait...\n")
r.recvline()
m = []
t = r.recvline().decode().strip()
print(f"{t=}")
print(t[0])
while(t[0] == "["):
print(f"{t=}")
m = parseMatrix(t, m)
t = r.recvline().decode().strip()
print(f"{m=}")
mat = Matrix(GF(127), m)
print(mat.multiplicative_order())
matOrd = str(mat.multiplicative_order())
r.sendline(matOrd)
print(r.recvall())
#b'| Congrats, you got the flag: CCTF{ma7RicES_4R3_u5EfuL_1n_PUbl!c-k3y_CrYpt0gr4Phy!}\n'
Flag : CCTF{ma7RicES_4R3_u5EfuL_1n_PUbl!c-k3y_CrYpt0gr4Phy!}
Baphomet

The source code :
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from base64 import b64encode
from flag import flag
def encrypt(msg):
ba = b64encode(msg.encode('utf-8'))
baph, key = '', ''
for b in ba.decode('utf-8'):
if b.islower():
baph += b.upper()
key += '0'
else:
baph += b.lower()
key += '1'
baph = baph.encode('utf-8')
key = int(key, 2).to_bytes(len(key) // 8, 'big')
enc = b''
for i in range(len(baph)):
enc += (baph[i] ^ key[i % len(key)]).to_bytes(1, 'big')
return enc
enc = encrypt(flag)
f = open('flag.enc', 'wb')
f.write(enc)
f.close()
Solve script :
from base64 import b64encode, b64decode
from Crypto.Util.number import *
#b64encode("CCTF{".encode('utf-8'))
#b'Q0NURns='
#Flip casing : b'q0nurN'
f = open('flag.enc', 'rb')
ct = f.read()
baph6 = b'q0nurN'
key = b''
for i in range(6):
key += long_to_bytes(baph6[i] ^ ct[i])
baph = b''
for i in range(len(ct)):
baph += (ct[i] ^ key[i % len(key)]).to_bytes(1, 'big')
rbaph = ''
for b in baph.decode('utf-8'):
if b.islower():
rbaph += b.upper()
else:
rbaph += b.lower()
print(b64decode(rbaph.encode('utf-8')))
#b'CCTF{UpP3r_0R_lOwER_17Z_tH3_Pr0bL3M}'
Flag : CCTF{UpP3r_0R_lOwER_17Z_tH3_Pr0bL3M}
SOTS
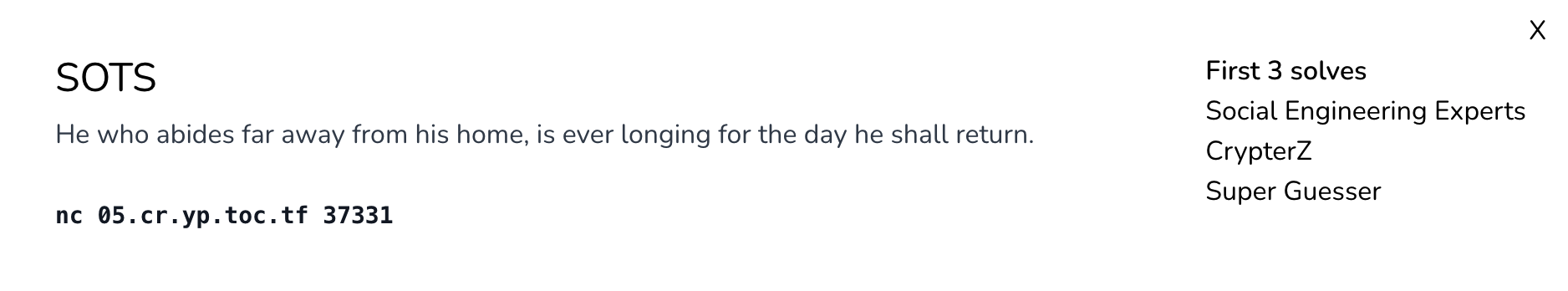
I used Alpertron’s online calculator to solve. Chall description and solve (got first blood) :
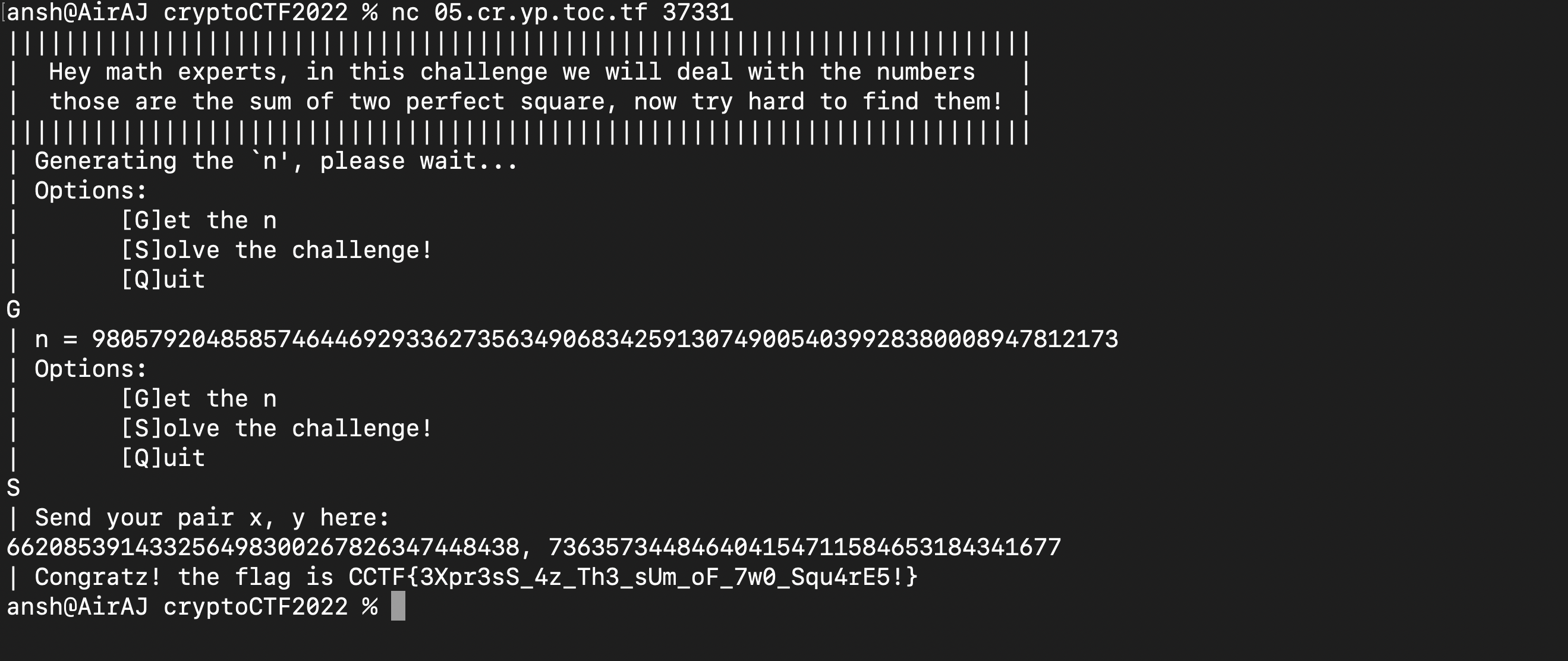
Flag : CCTF{3Xpr3sS_4z_Th3_sUm_oF_7w0_Squ4rE5!}
polyRSA

The source code :
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from flag import flag
def keygen(nbit = 64):
while True:
k = getRandomNBitInteger(nbit)
p = k**6 + 7*k**4 - 40*k**3 + 12*k**2 - 114*k + 31377
q = k**5 - 8*k**4 + 19*k**3 - 313*k**2 - 14*k + 14011
if isPrime(p) and isPrime(q):
return p, q
def encrypt(msg, n, e = 31337):
m = bytes_to_long(msg)
return pow(m, e, n)
p, q = keygen()
n = p * q
enc = encrypt(flag, n)
print(f'n = {n}')
print(f'enc = {enc}')
Solve script :
from Crypto.Util.number import *
n = 44538727182858207226040251762322467288176239968967952269350336889655421753182750730773886813281253762528207970314694060562016861614492626112150259048393048617529867598499261392152098087985858905944606287003243
ct = 37578889436345667053409195986387874079577521081198523844555524501835825138236698001996990844798291201187483119265306641889824719989940722147655181198458261772053545832559971159703922610578530282146835945192532
#k = var('k')
#print(solve([(k**6 + 7*k**4 - 40*k**3 + 12*k**2 - 114*k + 31377)*(k**5 - 8*k**4 + 19*k**3 - 313*k**2 - 14*k + 14011)==n], k))
k = 9291098683758154336
p = k**6 + 7*k**4 - 40*k**3 + 12*k**2 - 114*k + 31377
q = k**5 - 8*k**4 + 19*k**3 - 313*k**2 - 14*k + 14011
assert p*q == n
φ = (p-1) * (q-1)
e = 31337
d = pow(e, -1, φ)
print(long_to_bytes(pow(ct, d, n)))
#b'CCTF{F4C70r!N9_tRIcK5_aR3_fUN_iN_RSA?!!!}'
Flag : CCTF{F4C70r!N9_tRIcK5_aR3_fUN_iN_RSA?!!!}
Mic Check
Got second blood.
Flag : CCTF{Th3_B3sT_1S_Yet_t0_C0m3!!}