
I participated in Perfect Blue’s 2021 CTF over the weekend (Sat, 09 Oct. 2021, 08:00 SGT — Mon, 11 Oct. 2021, 08:00 SGT) playing as part of Social Engineering Experts. Me and Diamondroxxx managed to solve half of the crypto challs, the challenges were hard to say the least.
The level of difficulty was on par with Google CTF 2021, there were no sanity checks or survey challenges hence the number of scoring teams was greatly reduced. In the end, we ranked 32nd out of 210 scoring teams (there were 1535 registered teams).
Crypto was hard :(
Below are the writeups :
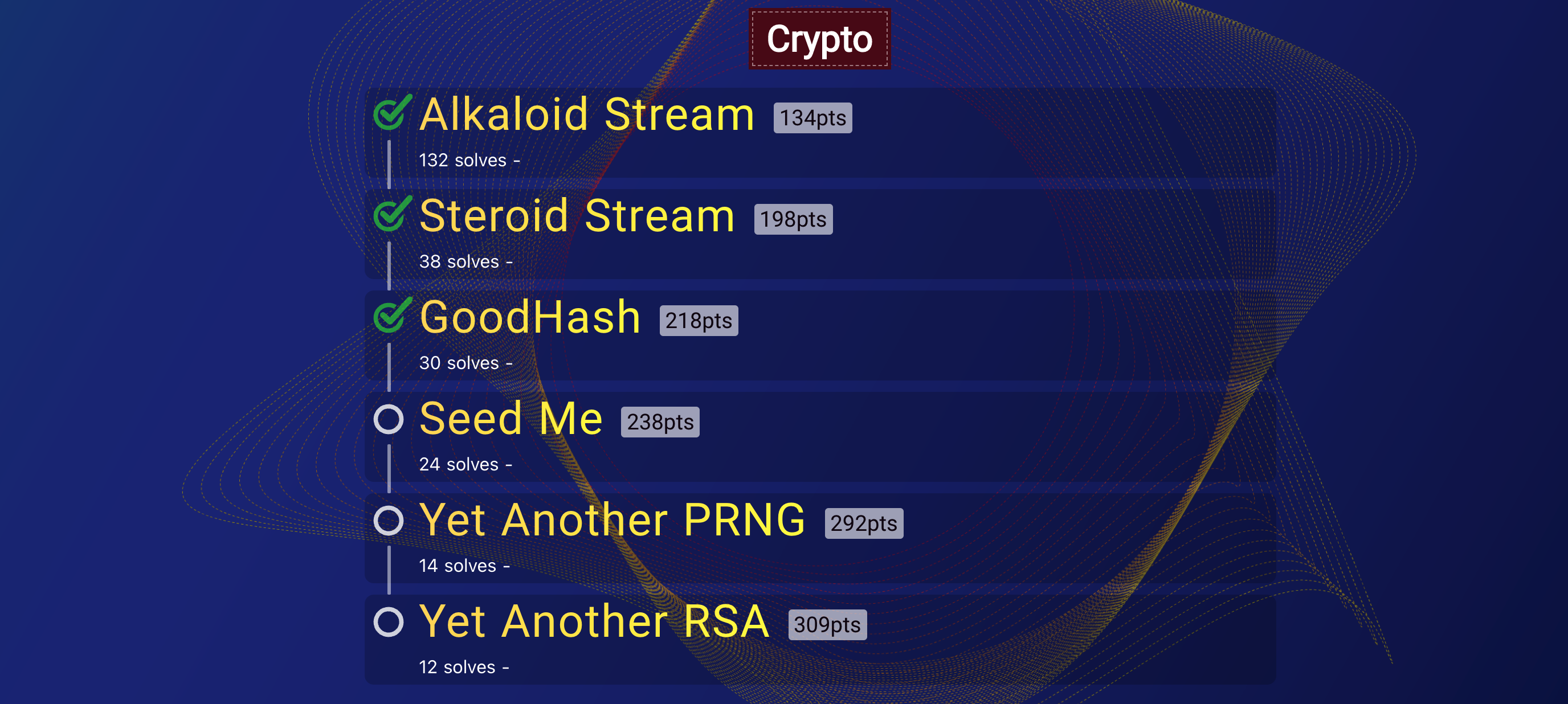
| Challenge | Category | Points | Solves |
|---|---|---|---|
| GoodHash | Crypto | 218 | 30 |
| Steroid Stream | Crypto | 198 | 38 |
| Ghost Writer | Misc | 170 | 58 |
| Alkaloid Stream | Crypto | 134 | 132 |
GoodHash
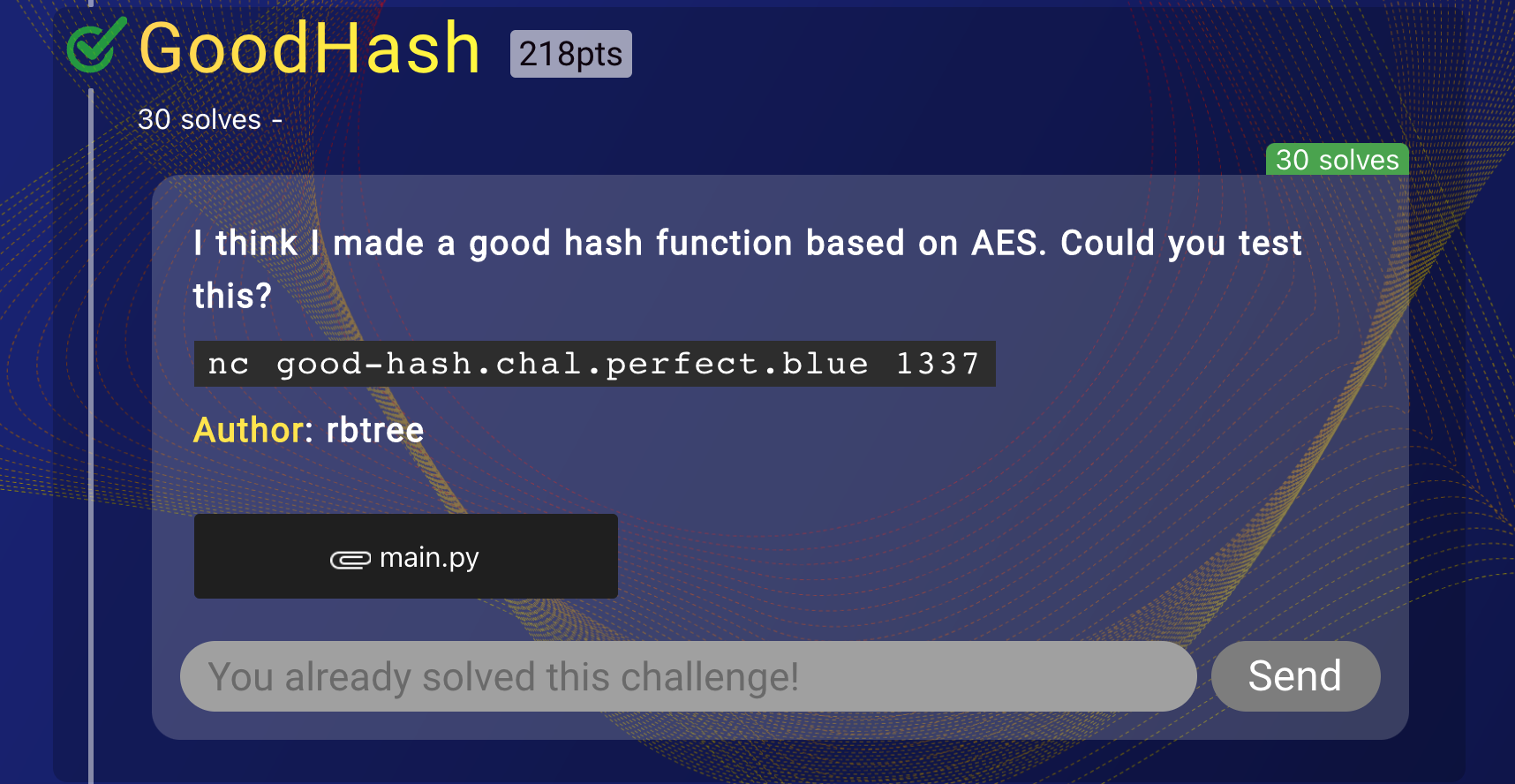
The server source code provided :
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from flag import flag
import json
import os
import string
ACCEPTABLE = string.ascii_letters + string.digits + string.punctuation + " "
class GoodHash:
def __init__(self, v=b""):
self.key = b"goodhashGOODHASH"
self.buf = v
def update(self, v):
self.buf += v
def digest(self):
cipher = AES.new(self.key, AES.MODE_GCM, nonce=self.buf)
enc, tag = cipher.encrypt_and_digest(b"\0" * 32)
return enc + tag
def hexdigest(self):
return self.digest().hex()
if __name__ == "__main__":
token = json.dumps({"token": os.urandom(16).hex(), "admin": False})
token_hash = GoodHash(token.encode()).hexdigest()
print(f"Body: {token}")
print(f"Hash: {token_hash}")
inp = input("> ")
if len(inp) > 64 or any(v not in ACCEPTABLE for v in inp):
print("Invalid input :(")
exit(0)
inp_hash = GoodHash(inp.encode()).hexdigest()
if token_hash == inp_hash:
try:
token = json.loads(inp)
if token["admin"] == True:
print("Wow, how did you find a collision?")
print(f"Here's the flag: {flag}")
else:
print("Nice try.")
print("Now you need to set the admin value to True")
except:
print("Invalid input :(")
else:
print("Invalid input :(")
The objective of this challenge is pretty straightforward. A known 61 byte IV (the random 16 bytes plus other formatting) is generated and used for encrypting 32 bytes of zeroes using AES-GCM with a known constant key. Our objective is to provide another IV which consists of only printable ASCII characters (from 32 to 126) such that when encrypting the 32 bytes of zeroes with the same key, the same ciphertext is generated. Also, the value of the admin key in our IV (as it is a dictionary) has to be set to be true instead of the false set by the server.
Hence we have to find a collision between the two IVs. The ciphertext generated is referred to as a hash in this challenge. This video by David Wong provides a very good introduction to how the GCM mode of operation works. More importantly, the document NIST SP 800-38D is especially useful because it fully explains all mechanisms underlying the GCM standard.
Reading the GCM specifications of the document (page 15), we can clearly see that if the length of the IV is not equal to 96 bytes as it is in our case (it is most commonly 96 bytes), a different mechanism for creating the IV is used. In that case:
\[\text{Let} \quad H \ = \ E_k(\text{16 bytes of zeroes})\] \[\text{Let} \quad s \ = \ (len(IV) \ mod \ 128)) \ mod \ 128\] \[J_0 \ = \ GHASH_H(IV \ \Vert \ 0^{s \ + \ 64} \ \Vert \ len(IV)_{64} \ )\]Here \( H \) is known as the hash subkey and it will always be constant as it is simply the block cipher encryption (in our case AES) of 16 bytes or 128 bits of zeroes. The block \( J_0 \) is the pre-counter block and is constructed such that the IV is padded with the minimum number of 0 bits until the result is a multiple of 16 bytes (the block size).
Obviously we are most interested in how the \(GHASH_H \) function works (hence the challenge name ‘GoodHash’) as if we can feed in two different IVs which can produce the same \( GHASH_H \), we would have produced two same ciphertexts and hence a collision (assuming the encryption key is constant as it is in our case) as long as the length of our different IV is the same as the original. This is due to the fact that the rest of the algorithm for GCM is the same for the two different IVs (as key, \( GHASH_H \), plaintext is constant).
Reading page 12 of the NIST documentation, the algorithm which defines \(GHASH_H \) is clearly outlined. Given the hash subkey \( H \), it is defined as follows:
\[Let \quad \ X \ = \ X_1 \ \Vert X_2 \ \Vert X_3 \ \Vert \ ... \ \Vert X_{i - 1} \ \Vert X_i \quad \text{where} \ X_i \ \text{corresponds to some block in a sequence}\] \[GHASH_H \quad = \quad (X_1 \cdot H^i) \ \oplus \ (X_2 \cdot H^{i - 1}) \ \oplus \ ... \ \oplus \ (X_{i - 1} \cdot H^2) \ \oplus \ (X_i \cdot H)\] \[\therefore GHASH_H \quad = \quad \sum_{i=1}^n \ X_i \ \cdot \ H^{n + 1 - i}\]Note that in GCM, our arithmetic operations are conducted in the field \( GF(2^{128}) \) where it is defined by the polynomial \( \ x^{128} \ + \ x^7 \ + \ x^2 \ + \ x \ + 1 \ \). Here the addition operation is equivalent to XOR as any finite field of characteristic 2 turns out to be the unique finite field of order 2n for some n (property of indempotence).
Given that definiton of \( GHASH_H \), we can hence produce collisions between two different IVs:
\[Let \quad IV \ = B_1 \ \Vert \ B_2 \ \Vert \ ... \ \Vert \ B_{i-1} \ \Vert B_i\]Here \( B_i \) corresponds to the blocks (16 bytes each) which constitute the IV as defined above. This is after performing the required padding as per the definition for the input into \( GHASH_H \) as shown above. For example, suppose we have these 61 bytes for the IV:
nonce = b'{"token": "013a87331ab2f704f9badf297f61b85f", "admin": false}'
Looking at the source code for pycryptodome’s GCM implementation and fixing a slight error, we managed to implement and test out the generation of \( J_0 \) and the \( GHASH_H \) with different values. This test file can be found here. This allowed us to create the appropriately padded nonce using the code below:
fill = (16 - (len(nonce) % 16)) % 16 + 8
ghash_in = (nonce + b'\x00' * fill + long_to_bytes(8 * len(nonce), 8))
Note that you can only run the GHASH function if you have an Intel based processor as CLMUL is an extension to the x86 instruction set which implements the multiplication of polynomials over the finite field \( GF(2) \) which speeds up the process of block cipher encryption using GCM (Galois Counter Mode).
As a result our nonce becomes:
ghash_in = b'{"token": "013a87331ab2f704f9badf297f61b85f", "admin": false}\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x01\xe8'
Hence since we have 5 blocks of 16 bytes (as the length is 80 bytes), we have:
\[Let \ IV \ = \ B_1 \ \Vert \ B_2 \ \Vert \ B_3 \ \Vert \ B_4 \ \Vert \ B_5\] \[\therefore J_0 \ = \ GHASH_H(IV) \ = \ B_1 \cdot H^5 \ + \ B_2 \cdot H^4 \ + \ B_3 \cdot H^3 \ + \ B_4 \cdot H^2 \ + \ B_5 \cdot H\]Using the token example above, let us divide it into blocks of 16 bytes:
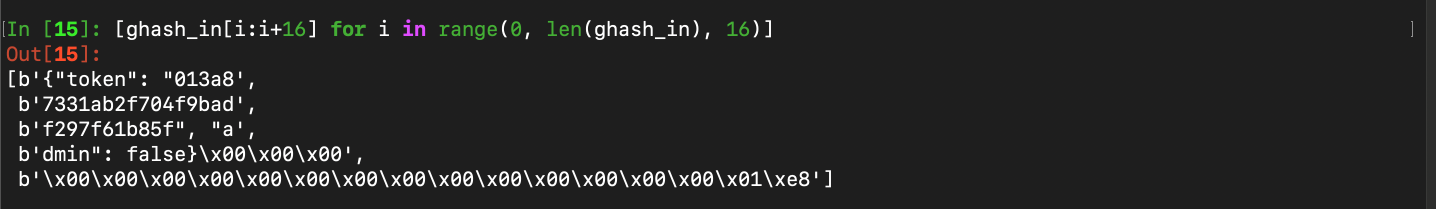
We can see from the 5 blocks above that we would want to change the second block (the one which is fully composed of some of the random 16 bytes in hex) as well as the fourth block as we would want to set the false to true. The rest of the blocks could remain the same, including the padding as the length of the different target IV should equal the original.
As a result, we can define our second target IV such that the \( J_0s \) are equal:
\[Let \ IV^I \ = \ B_1 \ \Vert \ B_2^I \ \Vert \ B_3 \ \Vert \ B_4^I \ \Vert \ B_5\] \[\therefore J_0 \ = \ GHASH_H^I(IV) \ = \ B_1 \cdot H^5 \ + \ B_2^I \cdot H^4 \ + \ B_3 \cdot H^3 \ + \ B_4^I \cdot H^2 \ + \ B_5 \cdot H\]By cancelling the common terms from the equations for \( GHASH_H(IV) \) and \( GHASH_H(IV^I) \) constructed above, we have:
\[B_2^I \cdot H^4 \ + \ B_4^I \cdot H^2 \ = \ B_2 \cdot H_4 \ + \ B_4 \cdot H^2\] \[B_2^I \cdot H^2 \ + \ B_4^I \ = \ B_2 \cdot H^2 \ + \ B_4\] \[\therefore B_2^I \ = \ \frac{B_2 \cdot \ H^2 \ - \ B_4^I}{H^2}\]Here since all terms on the right hand side are constant, by solving for \( B_2^I \), we would be able to find the correct configuration of bytes to change in block 2 in order to make the \( J_0s \) equal (note that the changed block 4 will always be constant as we know the true has to be changed to false). We can prove that this works by running the following test script in Sage (note that the file test.py referenced to earlier is used as the import) :
import os
from bitstring import BitArray, Bits
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from test import *
def bytes_to_element(val, field, a):
bits = BitArray(val)
result = field.fetch_int(0)
for i in range(len(bits)):
if bits[i]:
result += a^i
return result
P.<x> = PolynomialRing(GF(2))
p = x^128 + x^7 + x^2 + x + 1
GFghash.<a> = GF(2^128,'x',modulus=p)
key = b"goodhashGOODHASH"
hash_subkey = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB).encrypt(b'\x00'*16)
H_bf = bytes_to_element(hash_subkey, GFghash, a)
nonce = b'{"token": "d3271b732403d742fa1e617d24c741c8", "admin": false}'
fill = (16 - (len(nonce) % 16)) % 16 + 8
ghash_in = (nonce +
b'\x00' * fill +
long_to_bytes(8 * len(nonce), 8))
a1, a2, a3, a4, a5 = [ghash_in[i:i+16] for i in range(0, len(ghash_in), 16)]
assert all(len(b) == 16 for b in [a1, a2, a3, a4, a5])
a1_bf, a2_bf, a3_bf, a4_bf, a5_bf = [bytes_to_element(x, GFghash, a) for x in [a1, a2, a3, a4, a5]]
a4_prime_bf = bytes_to_element(b'dmin": true }', GFghash, a)
a2_prime_bf = (a2_bf*H_bf^2 + a4_bf - a4_prime_bf) / H_bf^2
a2_prime = long_to_bytes(BitArray(a2_prime_bf.polynomial().list()).uint)
a4_prime = long_to_bytes(BitArray(a4_prime_bf.polynomial().list()).uint)
print("-"*25 + "nonces" + "-"*25)
print(a1 + a2 + a3 + a4 + a5)
print(a1 + a2_prime + a3 + a4_prime + a5)
print("-"*25 + "computed hashes" + "-"*25)
print(long_to_bytes(BitArray((a1_bf*H_bf^5 + a2_bf*H_bf^4 + a3_bf*H_bf^3 + a4_bf*H_bf^2 + a5_bf*H_bf).polynomial().list()).uint))
print(long_to_bytes(BitArray((a1_bf*H_bf^5 + a2_prime_bf*H_bf^4 + a3_bf*H_bf^3 + a4_prime_bf*H_bf^2 + a5_bf*H_bf).polynomial().list()).uint))
assert a1_bf*H_bf^5 + a2_bf*H_bf^4 + a3_bf*H_bf^3 + a4_bf*H_bf^2 + a5_bf*H_bf == a1_bf*H_bf^5 + a2_prime_bf*H_bf^4 + a3_bf*H_bf^3 + a4_prime_bf*H_bf^2 + a5_bf*H_bf
print("-"*25 + "J0s" + "-"*25)
J0 = getJ0((a1 + a2 + a3 + a4)[:-3])
J0_PRIME = getJ0(a1 + a2_prime + a3 + a4_prime)
print(f"J0 is {J0}")
print(f"J0_PRIME is {J0_PRIME}")
assert J0 == J0_PRIME
print("-"*25 + "ciphertexts" + "-"*25)
CT1 = digest((a1 + a2 + a3 + a4)[:-3])
CT2 = digest(a1 + a2_prime + a3 + a4_prime)
print(f"CT1 is {CT1}")
print(f"CT2 is {CT2}")
assert CT1 == CT2
print("-"*25 + "New Nonce" + "-"*25)
print(f"New diff nonce is {a1 + a2_prime + a3 + a4_prime + a5}")
Running this script yields us this new nonce:
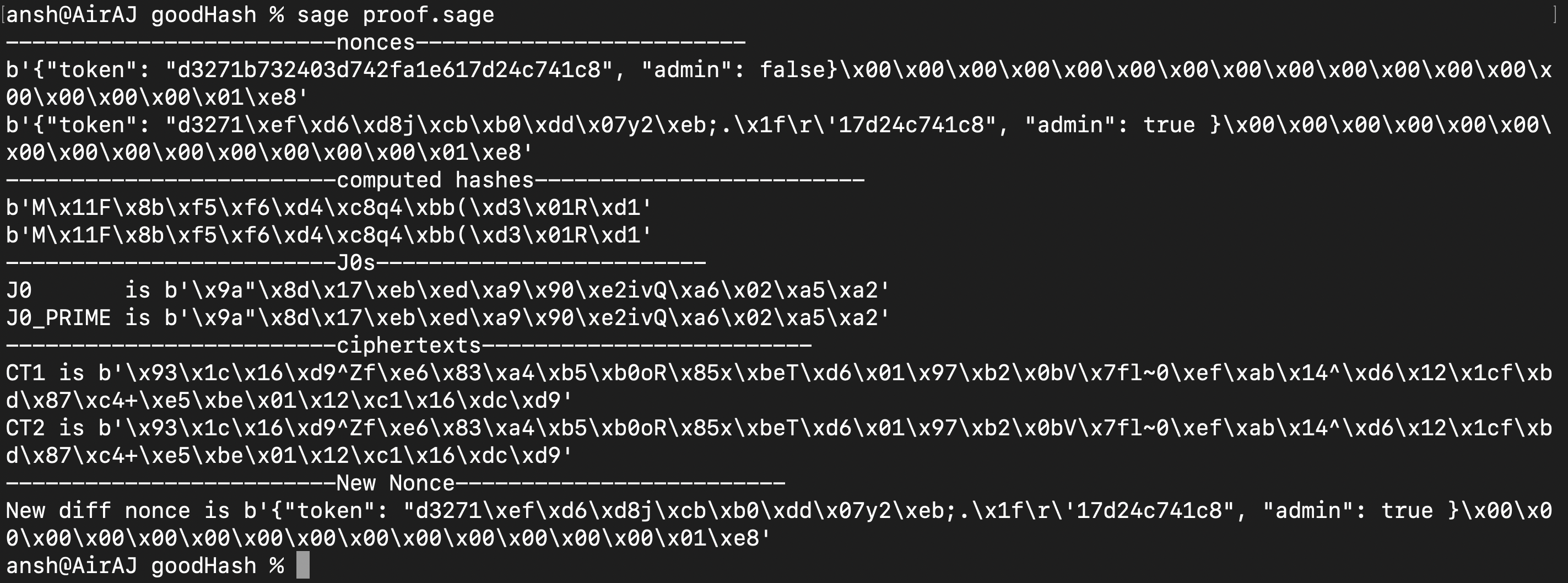
Great, so now we have a functioning program to generate the desired target IV (the new nonce). However there are two things to note. Firstly, this method does work most of the time but not always as the assertion for the \( J_0s \) fails at times (not too frequently). But that can be avoided by running the script with a new random nonce generated by the server a few more times.
Secondly and more importantly, the new IV that we have to provide must have only printable ASCII characters. The solution to the equation shown above does not guarantee that will always be the case as shown by the random unprintable bytes that we received. In fact nearly always, we would have these random bytes. Hence we would have to come up with a different way to generate a new valid IV.
What we thought of was replacing some of the bytes of block 3 randomly and then testing if a solution exists such that the bytes in block 2 are printable are ASCII printable. Let me explain better. We know that the structure for our block 3 is as follows :
block3 = b'f297f61b85f", "a'
Here the f297f61b85f represents the last 11 nibbles of the random 16 bytes generated by the server at the start. Now assume using the method above, we solved for the new IV which does produce a collision but is not made up of only printable ASCII characters. We can represent our block 3 as the 11 hex characters (nibbles) followed by ", "a which has to be constant.
Suppose we didn’t get a solution. What if we repeat the process by generating 5 random bytes ourselves (10 hex characters) and then appending a fixed hex character (in our case we used b) at the end? If we do that, we can again solve for the collision and check if the new block 2 is made up of only ASCII printable characters. Hence we can keep repeating this process until we do get a valid solution.
However this means that we cannot use our previous equation as now block 3 is also modified. Let us rewrite the equations and solve for the bytes needed in block 2 to generate a collision again :
\[J_0 \ = \ GHASH_H(IV) \ = \ B_1 \cdot H^5 \ + \ B_2 \cdot H^4 \ + \ B_3 \cdot H^3 \ + \ B_4 \cdot H^2 \ + \ B_5 \cdot H\] \[\therefore J_0 \ = \ GHASH_H^I(IV) \ = \ B_1 \cdot H^5 \ + \ B_2^I \cdot H^4 \ + \ B_3^I \cdot H^3 \ + \ B_4^I \cdot H^2 \ + \ B_5 \cdot H\]After equating the two equations, cancelling the common terms and dividing by \(H^2 \), we have :
\[B_2^I \cdot H^2 \ + \ B_3^I \cdot H \ + \ B_4^I \ = \ B_2 \cdot H^2 \ + \ B_3 \cdot H \ + \ B_4\] \[B_2^I \cdot H^2 \ + \ B_3^I \cdot H \ = \ B_2 \cdot H^2 \ + \ B_3 \cdot H \ + \ B_4 \ - \ B_4^I\] \[B_2^I \cdot H \ + \ B_3^I \ = \ \frac{ B_2 \cdot H^2 \ + \ B_3 \cdot H \ + \ B_4 \ - \ B_4^I}{H}\] \[Let \quad k \ = \ \frac{ B_2 \cdot H^2 \ + \ B_3 \cdot H \ + \ B_4 \ - \ B_4^I}{H}\] \[\therefore B_2^I \ = \ \frac{k \ - \ B_3^I}{H}\]What we did was as outlined above. We kept generating 5 bytes (10 hex characters) of \( B_3^I \) along with the constant ending until we can obtain a solution for \( B_2^I \) where all bytes are printable ASCII characters. We used multithreading to speed things up and changed the IV received from the server after trying 100,000 iterations of random 5 bytes for \( B_3^I \).
The reason why we used k to represent the values shown above is because all of those blocks were constants (including \( B_4^I \) as the false is simply changed to true). We also know that we ourselves will generate the 5 random bytes as well as the fixed hex character b for \( B_3^I \) but since this will always change until a solution is found, we chose to calculate the value of k outside the loop for increased efficiency.
For our solve script, we removed the \( J_0 \) assertion since sometimes it would not hold and used the same test.py file as mentioned above :
from bitstring import BitArray, Bits
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from test import *
from pwn import *
from tqdm import tqdm
import string
import os
from tqdm.contrib.concurrent import process_map, thread_map
debug = False
local = False
while True:
try:
if local:
r = process(["python3", "testServer.py"], level='debug') if debug else process(["python3", "testServer.py"])
else:
r = remote("good-hash.chal.perfect.blue", 1337, level = 'debug') if debug else remote("good-hash.chal.perfect.blue", 1337)
r.recvuntil('Body: ')
token = json.loads(r.recvline()[:-1].decode())['token']
r.recvuntil('Hash: ')
hash = r.recvline(keepends=False).decode()
nonce = json.dumps({"token": token, "admin": False}).encode()
print(f"Nonce fetched from server is {nonce}")
def bytes_to_element(val, field, a):
bits = BitArray(val)
result = field.fetch_int(0)
for i in range(len(bits)):
if bits[i]:
result += a^i
return result
P.<x> = PolynomialRing(GF(2))
p = x^128 + x^7 + x^2 + x + 1
GFghash.<a> = GF(2^128,'x',modulus=p)
key = b"goodhashGOODHASH"
hash_subkey = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB).encrypt(b'\x00'*16)
H_bf = bytes_to_element(hash_subkey, GFghash, a)
#nonce = b'{"token": "d3271b732403d742fa1e617d24c741c8", "admin": false}'
fill = (16 - (len(nonce) % 16)) % 16 + 8
ghash_in = (nonce +
b'\x00' * fill +
long_to_bytes(8 * len(nonce), 8))
a1, a2, a3, a4, a5 = [ghash_in[i:i+16] for i in range(0, len(ghash_in), 16)]
assert all(len(b) == 16 for b in [a1, a2, a3, a4, a5])
a1_bf, a2_bf, a3_bf, a4_bf, a5_bf = [bytes_to_element(x, GFghash, a) for x in [a1, a2, a3, a4, a5]]
a4_prime_bf = bytes_to_element(b'dmin": true }', GFghash, a)
k = (a2_bf*H_bf^2 + a4_bf + a3_bf*H_bf - a4_prime_bf) / H_bf
def iterate(n):
a3_prime, a3_prime_bf = a3, a3_bf
for i in tqdm(range(n)):
a2_prime_bf = (k - a3_prime_bf) / H_bf
a2_prime = long_to_bytes(BitArray(a2_prime_bf.polynomial().list()).uint)
a4_prime = long_to_bytes(BitArray(a4_prime_bf.polynomial().list()).uint)
if all(32 <= i <= 126 for i in a2_prime):
print("-"*25 + "nonces" + "-"*25)
print(a1, a2, a3, a4, a5)
print(a1, a2_prime, a3_prime, a4_prime, a5)
print("-"*25 + "computed hashes" + "-"*25)
print(long_to_bytes(BitArray((a1_bf*H_bf^5 + a2_bf*H_bf^4 + a3_bf*H_bf^3 + a4_bf*H_bf^2 + a5_bf*H_bf).polynomial().list()).uint))
print(long_to_bytes(BitArray((a1_bf*H_bf^5 + a2_prime_bf*H_bf^4 + a3_prime_bf*H_bf^3 + a4_prime_bf*H_bf^2 + a5_bf*H_bf).polynomial().list()).uint))
assert a1_bf*H_bf^5 + a2_bf*H_bf^4 + a3_bf*H_bf^3 + a4_bf*H_bf^2 + a5_bf*H_bf == a1_bf*H_bf^5 + a2_prime_bf*H_bf^4 + a3_prime_bf*H_bf^3 + a4_prime_bf*H_bf^2 + a5_bf*H_bf
print("-"*25 + "ciphertexts" + "-"*25)
CT1 = digest((a1 + a2 + a3 + a4)[:-3])
CT2 = digest(a1 + a2_prime + a3_prime + a4_prime)
print(f"CT1 is {CT1}")
print(f"CT2 is {CT2}")
try:
assert CT1 == CT2
except AssertionError as e:
print(e)
continue
nonceToSend = a1 + a2_prime + a3_prime + a4_prime
print("-"*50)
print(f"Nonce to send is {nonceToSend}")
print(" "*20+"Getting flag, fingers crossed ...... :) ")
r.sendlineafter('> ', nonceToSend)
print(r.recvall())
else:
a3_prime = os.urandom(5).hex().encode() + b'b", "a'
a3_prime_bf = bytes_to_element(a3_prime, GFghash, a)
thread_map(iterate, [10000]*10, max_workers=150)
except AssertionError:
print("Loop Ran Out!!!")
continue
We used 3 different computers to maximise our chances and eventually after around half an hour, we managed to obtain a solution (note that the fast, extensible progress bar tqdm was used which accounts for some of the messy formatting once a solution was obtained):
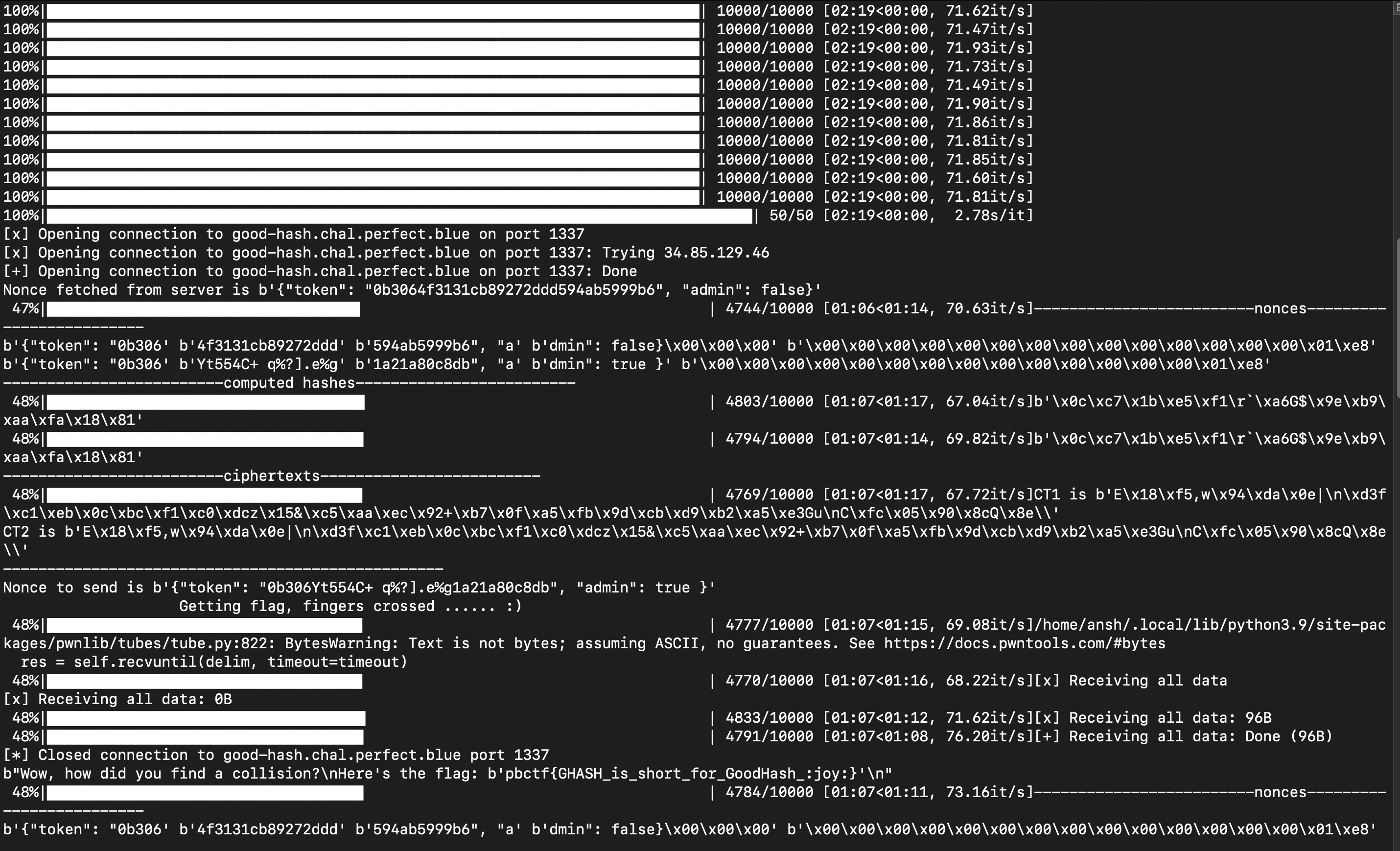
Flag : pbctf{GHASH_is_short_for_GoodHash_:joy:}
Steroid Stream
The source code provided :
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import random
from flag import flag
def keygen(ln):
# Generate a linearly independent key
arr = [ 1 << i for i in range(ln) ]
for i in range(ln):
for j in range(i):
if random.getrandbits(1):
arr[j] ^= arr[i]
for i in range(ln):
for j in range(i):
if random.getrandbits(1):
arr[ln - 1 - j] ^= arr[ln - 1 - i]
return arr
def gen_keystream(key):
ln = len(key)
assert ln > 50
# Generate some fake values based on the given key...
fake = [0] * ln
for i in range(ln - ln // 3):
arr = list(range(i + 1, ln))
random.shuffle(arr)
for j in arr[:ln // 3]:
fake[i] ^= key[j]
# Generate the keystream
res = []
for i in range(ln):
t = random.getrandbits(1)
if t:
res.append((t, [fake[i], key[i]]))
else:
res.append((t, [key[i], fake[i]]))
# Shuffle!
random.shuffle(res)
keystream = [v[0] for v in res]
public = [v[1] for v in res]
return keystream, public
def xor(a, b):
return [x ^ y for x, y in zip(a, b)]
def recover_keystream(key, public):
st = set(key)
keystream = []
for v0, v1 in public:
if v0 in st:
keystream.append(0)
elif v1 in st:
keystream.append(1)
else:
assert False, "Failed to recover the keystream"
return keystream
def bytes_to_bits(inp):
res = []
for v in inp:
res.extend(list(map(int, format(v, '08b'))))
return res
def bits_to_bytes(inp):
res = []
for i in range(0, len(inp), 8):
res.append(int(''.join(map(str, inp[i:i+8])), 2))
return bytes(res)
flag = bytes_to_bits(flag)
key = keygen(len(flag))
keystream, public = gen_keystream(key)
assert keystream == recover_keystream(key, public)
enc = bits_to_bytes(xor(flag, keystream))
print(enc.hex())
print(public)
The attached output.txt file can be found here.
By testing the encryption scheme, one can observe that every non-zero term in a pair of a public key where one term is zero is part of the flag. Using this process, one can recover approximately a third of the numbers in the key. After that, by looping through the remaining pair of the public key, due to how the fake values are generated based on the given key in gen_keystream, there must exist some pair in the remaning pairs of the public key where one value in the pair is linearly dependent on the current key and the other is linearly independent. The value which provides this dependence is added to the current key and the selected pair is removed from the list of remaining pairs. The iteration continues until all remaining pairs are exhausted.
After that we can reconstruct the keystream from the current key as the bit would be 1 if it exists in the current key else it would be 0 and from there we can XOR the keystream and encrypted text to get the flag.
The Sage solve script :
import ast
from tqdm import tqdm
with open("output.txt", "r") as f:
temp = f.readlines()
def xor(a, b):
return [x ^^ y for x, y in zip(a, b)]
def bytes_to_bits(inp):
res = []
for v in inp:
res.extend(list(map(int, format(v, '08b'))))
return res
def bits_to_bytes(inp):
res = []
for i in range(0, len(inp), 8):
res.append(int(''.join(map(str, inp[i:i+8])), 2))
return bytes(res)
enc = bytes_to_bits(bytes.fromhex("792137ecd08d478208e850a60680ccb7e937778222b1ceb8a1ac89046f421706930d240300cdf3ed07691c14a5ed60b226841238fee420feda73174021a557f552b5181dfb717aee329c44b90a"))
public = ast.literal_eval(temp[1])
#enc = bytes_to_bits(bytes.fromhex("f1558b8a3b"))
#public = [[0, 1071488838234], [65204354650, 1021669646129], [57666690108, 711988189457], [552902666172, 573828359780], [0, 213492007909], [961253271207, 727103715548], [385906222855, 943229752996], [16610212448, 48587962307], [499126049781, 0], [139307930864, 0], [29296352379, 377265293573], [683961828786, 814349401820], [536270470756, 0], [422540082809, 591630079875], [707791955581, 894791470441], [753162308727, 300617045692], [325979509102, 213740380088], [196990823610, 1011199229148], [1088167842249, 1074057466982], [85729246474, 751316447276], [1071251091857, 0], [961701127210, 732048561777], [927365395478, 614368622730], [716610958274, 0], [433179696788, 293615215737], [925315086770, 317181845965], [0, 928242444496], [722653918199, 717251183911], [0, 446349369016], [39814622639, 0], [908503739383, 0], [41753962425, 996494081092], [1067021348692, 597325539631], [749045473382, 344345566050], [820380477164, 19121820088], [293108235585, 35969873245], [337685520602, 0], [0, 169031717508], [294197399814, 205188886661], [305394740869, 769041635555]]
for i in range (len(public)):
public[i][0] = Integer(public[i][0])
public[i][1] = Integer(public[i][1])
BITLENGTH = len(public)
B = Integers(2)^BITLENGTH
def are_dependent(vecs):
veclist = [B(v.bits() + [0]*(BITLENGTH - len(v.bits()))) for v in vecs]
return B.are_linearly_dependent(veclist)
with_zeros = list(filter(lambda p: 0 in p, public))
the_rest = list(filter(lambda p: 0 not in p, public))
print(len(with_zeros), len(the_rest))
key = [p[0] if p[1] == 0 else p[1] for p in with_zeros]
for i in range(len(the_rest)):
print(i)
for p in tqdm(the_rest):
print(".", end="")
if are_dependent(key + [p[0]]):
key += [p[1]]
the_rest.remove(p)
break
elif are_dependent(key + [p[1]]):
key += [p[0]]
the_rest.remove(p)
break
print()
keystream = [1 if pair[1] in key else 0 for pair in public]
print(bits_to_bytes(xor(enc, keystream)))
#pbctf{I_hope_you_enjoyed_this_challenge_now_how_about_playing_Metroid_Dread?}
The solve script took approximately 15 hours to run and was made bearable because of the awesomeness of tqdm which we wished we discovered sooner :
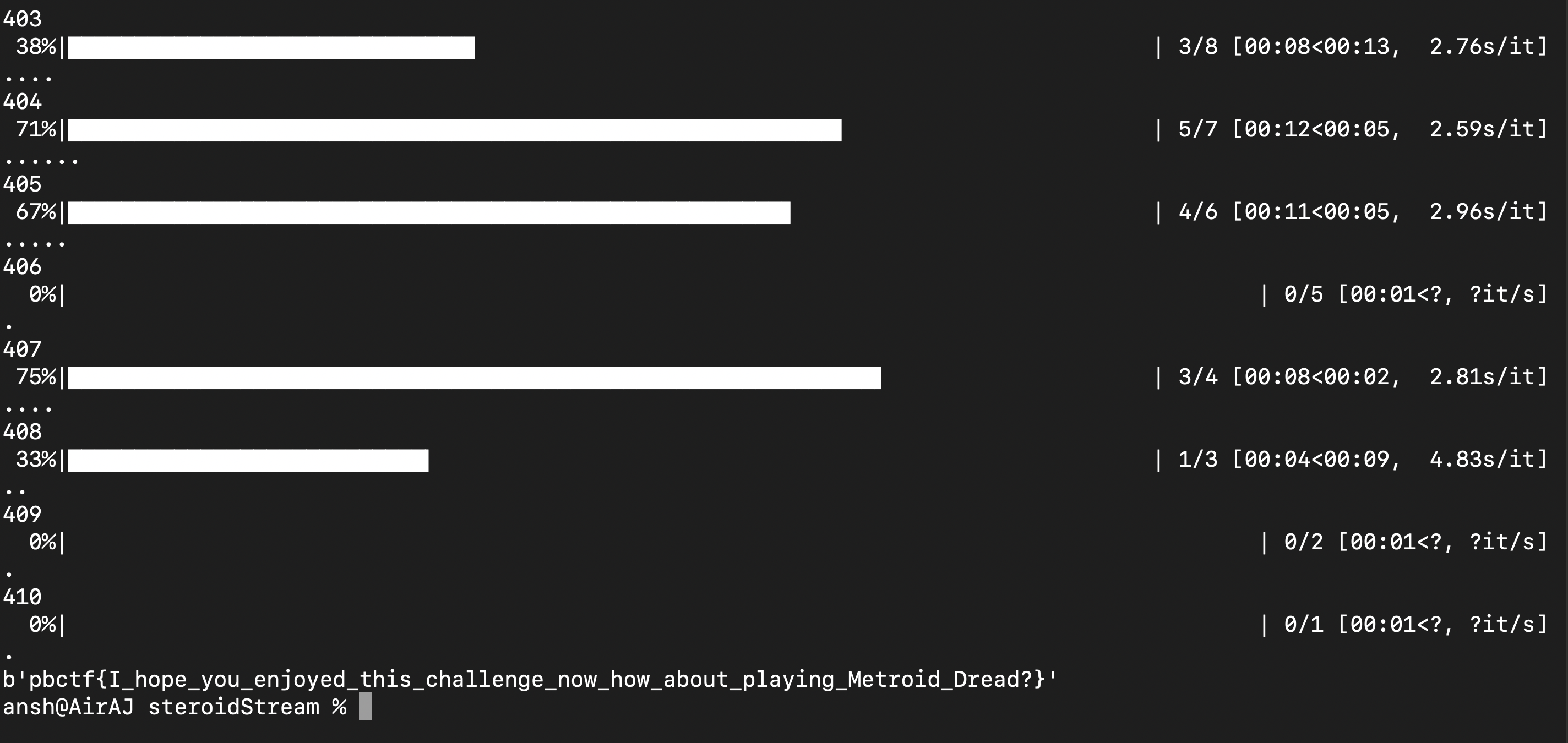
Flag : pbctf{I_hope_you_enjoyed_this_challenge_now_how_about_playing_Metroid_Dread?}
Ghost Writer
The attached zip can be found here. The challenge description is pretty much self-explanatory. We used the audio data analyzer keytap 1 which is extremely well suited for this job. We first provided known keyboard noises and the corresponding text input using the Cherry MX Vlue PBT keycaps official pack in mechvibes which sounds really similar to the given file and then used keytap on the actual given file to find the words.
Flag : pbctf{mechanical_keyboards_are_loud}
Alkaloid Stream
The source code provided :
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import random
from flag import flag
def keygen(ln):
# Generate a linearly independent key
arr = [ 1 << i for i in range(ln) ]
for i in range(ln):
for j in range(i):
if random.getrandbits(1):
arr[j] ^= arr[i]
for i in range(ln):
for j in range(i):
if random.getrandbits(1):
arr[ln - 1 - j] ^= arr[ln - 1 - i]
return arr
def gen_keystream(key):
ln = len(key)
# Generate some fake values based on the given key...
fake = [0] * ln
for i in range(ln):
for j in range(ln // 3):
if i + j + 1 >= ln:
break
fake[i] ^= key[i + j + 1]
# Generate the keystream
res = []
for i in range(ln):
t = random.getrandbits(1)
if t:
res.append((t, [fake[i], key[i]]))
else:
res.append((t, [key[i], fake[i]]))
# Shuffle!
random.shuffle(res)
keystream = [v[0] for v in res]
public = [v[1] for v in res]
return keystream, public
def xor(a, b):
return [x ^ y for x, y in zip(a, b)]
def recover_keystream(key, public):
st = set(key)
keystream = []
for v0, v1 in public:
if v0 in st:
keystream.append(0)
elif v1 in st:
keystream.append(1)
else:
assert False, "Failed to recover the keystream"
return keystream
def bytes_to_bits(inp):
res = []
for v in inp:
res.extend(list(map(int, format(v, '08b'))))
return res
def bits_to_bytes(inp):
res = []
for i in range(0, len(inp), 8):
res.append(int(''.join(map(str, inp[i:i+8])), 2))
return bytes(res)
flag = bytes_to_bits(flag)
key = keygen(len(flag))
keystream, public = gen_keystream(key)
assert keystream == recover_keystream(key, public)
enc = bits_to_bytes(xor(flag, keystream))
print(enc.hex())
print(public)
The attached output.txt file can be found here
Very similar to Steroid Stream except the solution is much easier. By observation, one can notice that the non-zero term in the public key pair with a 0 in it would correspond to the last term in the key. From there, within the first third of the public key, one can find the value same non-zero value but with a different non-zero number in its pair. By XORing those two numbers, the resultant number can be also found in another pair in the first third of the key. Hence by iteratively XORing the previous two numbers in the pair and searching for the resulting value, one can recover the keystream and hence the flag in the same manner as Steroid Stream.
The Sage solve script :
import ast
def xor(a, b):
return [x ^^ y for x, y in zip(a, b)]
def bytes_to_bits(inp):
res = []
for v in inp:
res.extend(list(map(int, format(v, '08b'))))
return res
def bits_to_bytes(inp):
res = []
for i in range(0, len(inp), 8):
res.append(int(''.join(map(str, inp[i:i+8])), 2))
return bytes(res)
with open("output.txt", "r") as f:
temp = f.readlines()
enc = bytes_to_bits(bytes.fromhex("cd4c1a7edd7a421dcea72ae8bf47946d74f6cdba763a6a052a3f2955333dc6fa267f5297c405bf807e922380ebf9628194bf319e8ae4074dc5476de1d81a52d72c29f0e8b590ac8f6a78bb"))
public = ast.literal_eval(temp[1])
for i in range (len(public)):
public[i][0] = Integer(public[i][0])
public[i][1] = Integer(public[i][1])
def get_pair(n):
ind = flatten(public).index(n) // 2
pair = public[ind]
if 0 in pair and n != 0:
pair = public[ind+1:][flatten(public[ind+1:]).index(n) // 2]
return pair
pair = get_pair(0)
key = [pair[0] if pair[1] == 0 else pair[1]]
#print(len(public))
for _ in range(len(public) - 1):
#print(_, pair)
to_find = reduce(lambda a, b: a ^^ b, key[:len(public)//3])
pair = get_pair(to_find)
key = [pair[0] if pair[1] == to_find else pair[1]] + key
#print(key)
keystream = [1 if pair[1] in key else 0 for pair in public]
print(bits_to_bytes(xor(enc, keystream)))
#b'pbctf{super_duper_easy_brute_forcing_actually_this_one_waq_made_by_mistake}'
#Flag should be (the q in 'waq' should be 'was'):
#pbctf{super_duper_easy_brute_forcing_actually_this_one_was_made_by_mistake}
Flag : pbctf{super_duper_easy_brute_forcing_actually_this_one_was_made_by_mistake}